Mastering cyber security audits: Your shield in the digital realm
Cyber security is a paramount concern for businesses and organisations of all sizes, and it should be a personal priority as well. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks underscore the importance of regularly assessing and improving cyber security not only in business environments but also within our homes. With the evolving landscape of remote work, the attack surface – the ways in which our systems can be compromised – is expanding.
A cyber security audit is a crucial tool that should be part of everyone’s cyber security defense plan. It helps identify vulnerabilities in our systems and data, guiding us on how to address them. In this article, we will explore best practices for conducting a cyber security audit.
At its core, a cyber security audit involves a comprehensive examination of information systems, policies, and procedures to assess the effectiveness of security controls. The ultimate goal is to identify vulnerabilities, threats, and risks that could compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data. While this may seem complex, applying a structured process can make it more manageable.
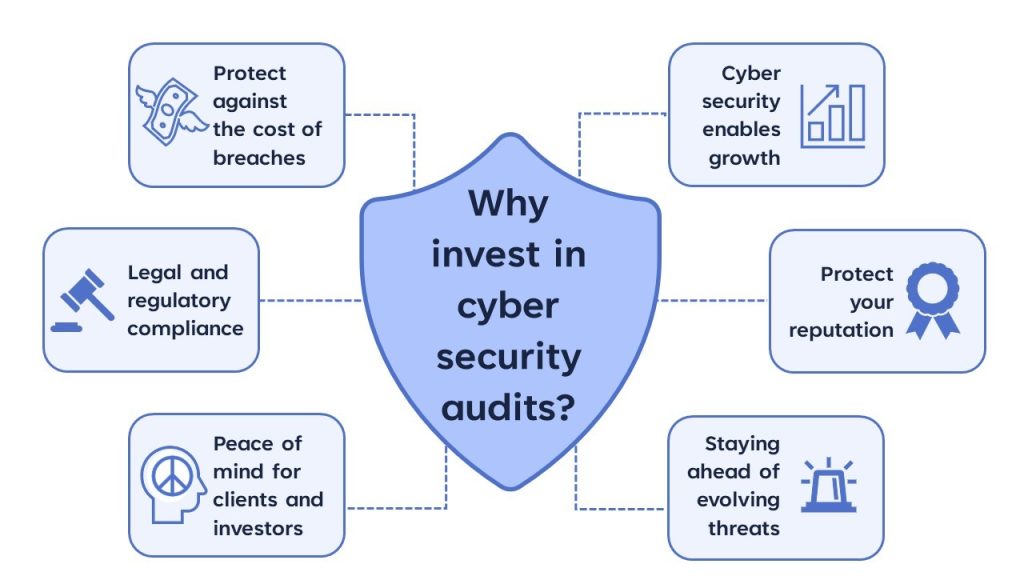
Why are cyber security audits important?
Cyber security audits are indispensable in today’s digital landscape.
Steps for conducting a cyber security audit
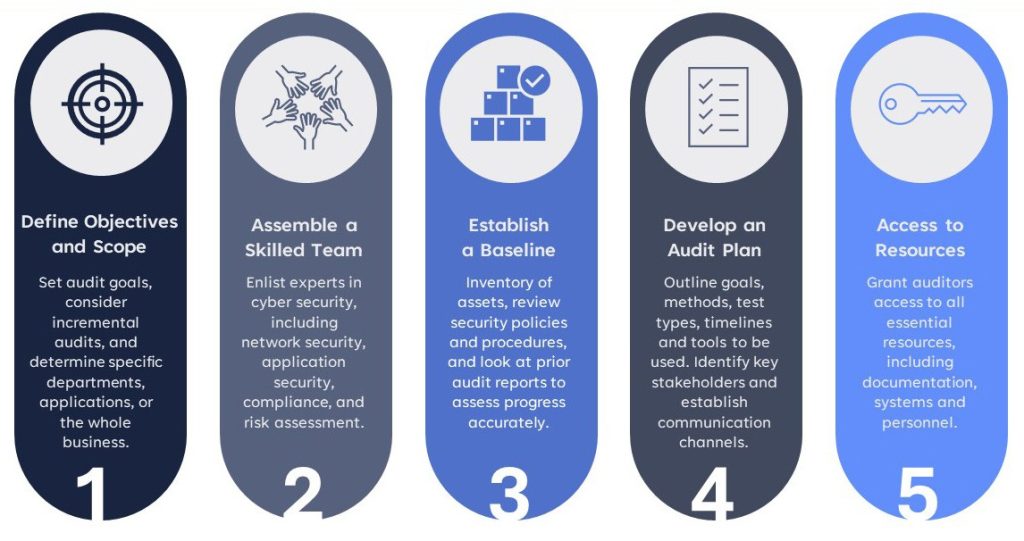
To ensure the success of your cyber security audit, it’s crucial not to approach it ‘off the cuff.’ Similar to managing any project, defining clear objectives and the scope of the audit is essential as it sets the boundaries and expectations.
Before starting, understanding your current status is vital for measuring progress. Keep in mind the famous cyber security adage, ‘You can’t protect what you don’t know about.’
Building a skilled team is a key to success, whether for a business audit that requires various cyber security experts or a personal audit where seeking help from knowledgeable individuals and engaging the entire household unit to divide tasks into manageable parts is a wise approach.
Moreover, cooperation from various departments is essential for a comprehensive audit, and the same principle applies at home, where involving all family members is crucial for an effective audit. Consider the wealth of knowledge and peace of mind you’ll acquire by tackling this task together.
Best practices for conducting a cyber audit
With your preparations complete, it’s time to dive into the practical aspects of the audit, focusing on best practices:
- Identify assets:
Remember, you cannot protect what you do not know about. This includes hardware, software (applications), data, and personnel. Creating an inventory of assets is essential for understanding what needs protection. It also establishes un understanding of exactly what is passing data across your network. An infected or vulnerable device on a network potentially exposes that network to compromise. One compromised device can lead to a malicious actor being able to move to other devices connected to that network. Another, often unknown weakness on a network are vulnerable or malicious applications. A device connected to your network with a malicious piece of software or application can also enable movement across other devices. So, identifying both physical assets (devices) and digital assets (software) on those devices is the critical first step. - Risk assessment:
Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. Assess the likelihood and potential impact of various security incidents. This step helps prioritise security measures. For example, unidentified assets may be found on your network. What risks do they pose if they remain unidentified and therefore not assessed. - Review policies and procedures:
In a business context, examine existing security policies and procedures to ensure alignment with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Evaluate employee adherence to these policies and make necessary updates. - Vulnerability scanning:
There are open source and enterprise vulnerability scanning tools to identify weaknesses in your systems and networks. These tools help pinpoint software vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and potential entry points for attackers. - Penetration testing:
A business audit may benefit from penetration testing, or ethical hacking, which involves a deeper more manual assessment, identification of vulnerabilities and actual exploitation of vulnerabilities. This goes beyond vulnerability scanning by actively trying to exploit weaknesses in a controlled manner. - Compliance checks:
Verify that your business complies with relevant laws and regulations such as the Australian Privacy Principles. If your business collects card payments or a service provider does on the business behalf, ensure there is compliance with the payment card industry security standards. Non-compliance can lead to legal consequences and fines. - Data security:
Classifying and protecting sensitive data is paramount. Ensure that data encryption, access controls, and data retention policies are in place and effective. Assess the security of data at rest and in transit. This extends to personal data being stored on public cloud infrastructures such as OneDrive, DropBox etc. Check data encryption settings as these may not be enabled by default. - Employee training and awareness:
The human element is still the weakest link in cyber security. Provide ongoing employee training and awareness programs, keeping staff informed about security best practices and potential threats. In home networks, ensure that all family members understand basic cyber security hygiene. - Incident response plan:
Evaluate the incident response and disaster recovery plans. Ensure they are well-documented, up-to-date, and that employees understand their roles in the event of a security incident. Implement secure data backup processes for home networks. - Security architecture:
Review the architecture of your network and systems. Ensure that security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and authentication mechanisms, are properly configured and effective. Consider establishing a guest network for added security on home networks. - Patch management:
Implement a patch management system to keep software up to date, addressing vulnerabilities. Encourage family members to keep their devices updated for home network security. - Third-party risk:
Evaluate the cyber security practices of third-party vendors and partners before allowing onto your network. The security of your business can be compromised through their vulnerabilities. Do your due diligence and ask for and assess their security controls. Ensure that contracts include cyber security requirements. - Continuous monitoring:
Cyber security is an ongoing process. Implement continuous monitoring to detect and respond to threats in real-time. This includes network monitoring, log analysis, and threat intelligence feeds. Your home network administrator can show what devices are connected and regularly auditing can show any suspicious devices. - Reporting and documentation:
Document the audit findings and create a comprehensive report. This report should include identified vulnerabilities, their severity, and recommendations for remediation. - Remediation:
Collaborate with the business to address identified vulnerabilities and weaknesses, prioritising and implementing changes to enhance overall security. - Follow-up:
Cyber security is dynamic, and threats are continually evolving. Conduct regular follow-up audits to ensure that security measures remain effective and up-to-date.
In conclusion
Cyber security audits are crucial in our interconnected digital world to safeguard business assets and personal data. Following best practices and staying informed about cyber security developments helps individuals and organisations proactively address security risks.
Remember, this is an ongoing effort, requiring continuous improvement and adaptation to emerging threats. Staying educated about cyber security is as vital as conducting audits. Regular cyber security audits, along with a strong incident response plan and a well-informed workforce, keep you ahead of evolving cyber threats.
These audits are a key part of a robust security strategy, offering valuable insights into a network’s security posture. By adhering to best practices in preparation, execution, and follow-up, you can bolster your cyber security defenses and protect sensitive data from potential threats.






